How Does a Plant Control Turgor Pressure
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in all higher plant cells. There are seven essential micronutrients in plants.
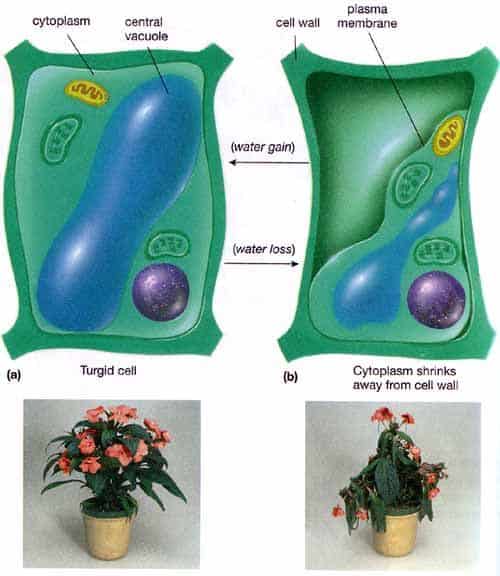
Turgor Pressure In Plants Examples And Meaning Jotscroll
By definition succulent plants are drought resistant plants in which the leaves stem or roots have become more than usually fleshy by the development of water-storing tissue.

. Boron B Zinc Zn Manganese Mn Iron Fe Copper Cu Molybdenum Mo Chlorine Cl are some of the important micronutrients in plants. Mimosa pudica from Latin. Other sources exclude roots as in the definition a plant with thick fleshy and swollen stems andor leaves adapted to dry environments.
The formation of starch from sugar in the sink increases the osmotic concentration. These organelles contain the plant cells chlorophyll responsible for the plants green color and the ability to absorb energy from sunlight. Also called sensitive plant nun-nighs plantsleepy plant action plant touch-me-not shameplant is a creeping annual or perennial flowering plant of the pealegume family FabaceaeIt is often grown for its curiosity value.
Pudica shy bashful or shrinking. This turgor pressure is responsible for the crispness of fresh vegetables. Chloroplast plant cells only.
This difference affects the relationship between succulents and. Some nutrients control the permeability of a cell membrane and some other control the osmotic pressure buffer action etc. Water is actively transported into the source region.
The pressure in the phloem of a root is normally greater than the pressure in the phloem of a leaf. The compound leaves fold inward and droop when touched or shaken defending themselves from.

Turgor Pressure Plant Cells Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Turgor Pressure Definition Characteristics And Examples

Turgor Pressure Heterogeneity Emerges From Cell Topology A Schematic Download Scientific Diagram
0 Response to "How Does a Plant Control Turgor Pressure"
Post a Comment